Permission Manager (.NET)
In Relativity, you can manage varying levels of security for users, system admins, and individual objects, such as views, tabs, and fields, across your instance of Relativity and in each workspace. You can also define custom permissions for Relativity Dynamic Objects (RDOs).
The Services API supports a set of operations for assigning system-defined permissions on the admin, workspace, and item level. You can manipulate either arbitrary sets of individual permissions, or entire admin, workspace, or item permission sets. Note that the logic for working with entire permission sets closely follows the logic of the Relativity permissions UI.
While you can't modify the system-defined permissions, you can programmatically create, update, and delete custom permissions for RDOs. You can perform read and query operations on both system-defined permissions and custom permissions. All operations on permissions are performed asynchronously.
You can also work with permissions using the Relativity REST API.
Permissions fundamentals
Before programmatically interacting with Relativity permissions, familiarize yourself with the Relativity permissions user interface. For more information, see
Follow these basic guidelines when working with permissions:
- Permissions are assigned to groups. Users inherit the highest level permissions based on group membership.
- Permissions are assigned on the admin level, workspace level, or individual item level.
- Permissions on admin and workspace level are assigned for each object type: For example, permission to work with Matter objects on the admin level or permission to work with documents on the workspace level.
- Permissions can be assigned to admin and workspace actions.
- Permissions can include subpermissions: for example, Document object subpermissions include Print/Save As PDF, Highlight Document, and Add and Delete Images.
- When programmatically interacting with permissions, you must use appropriate credentials (credentials with permissions to manage permissions). If you use insufficient credentials when working with permissions, nothing is returned.
-
Depending on your application's requirements, you can manipulate either arbitrary sets of individual permissions, or entire admin, workspace, or item permission sets. For more information, see Work with individual permissions, Add and remove groups to permissions, Enable item-level security, and Set group permissions
- The objects for working with Permissions described in this section are included in the Relativity.Services.Permission namespace. For more information, see Class library reference.
Typical use cases
The following are some typical use cases of programmatic interaction with permissions by a Relativity application developer or administrator.
Modify permissions for a group
Scenario: Modify selected permissions for users in a group.
- Use the SetPermissionSelectedForGroupAsync() method of the of the IPermissionManager interface.
- Input: Workspace ID, Group DTO, permission values
- Output: Silent success
For more information, see Set permission values.
Apply item level security for specific objects
Scenario: Apply Item level security by removing a group from a workspace field's permissions.
- Use QueryAsync() to filter down to the field you are interested in.
- Use SetItemLevelSecurityAsync() to enable item-level security.
- Use AddRemoveItemGroupsAsync() to remove specific group from the field's permissions.
- Input: Workspace ID, Field ID, Group ID
- Output: Silent success
For multiple artifacts and multiple workspaces, repeat the steps above as needed.
For more information, see Query permissions, Enable item-level security, and Add and remove groups to permissions.
Get Permissions for logged in user
Scenario: For a given user who is a member of multiple groups, find the highest level of permissions granted to determine what objects in a workspace to display.
The operations assume the context for the logged in user.
- Use QueryAsync() to filter down the list of permissions.
- Use GetPermissionSelectedAsync() to find the highest level of permissions granted to the user.
- Input: Workspace ID, permissions list
- Output: Permission list with associated values (true or false)
For more information, see Query permissions and Read the current user and group permission values.
Work with individual permissions
You can read and query individual permissions, check if the current user or a specified group have certain permissions, and set individual permissions for a group.
Permission objects
Use the following objects to interact Relativity permissions:
- PermissionRef
- Permission
- PermissionValue
- PermissionType
PermissionRef
An individual permission is identified by the PermissionRef class. PermissionRef contains these properties:
- ArtifactType Artifact type identifier of the artifact associated with the permission. The artifact type can be identified by the ArtifactTypeID or GUIDs. For example, a document permission would have the ArtifactTypeID value of 10.
- Name Name of the permission. The value is displayed by the Relativity permissions UI.
- PermissionID Unique permission identifier within a Relativity instance.
- PermissionType The type of Relativity permission represented by the PermissionType object.
PermissionRef is used for identifying permissions passed as input parameters to the GetPermissionSelectedAsync() and GetPermissionSelectedForGroupAsync() methods of the IPermissionManager interface. PermissionRef identifies a permission using the following:
- PermissionID
- ArtifactTypeID or ArtifactTypeGuids and Name
- ArtifactTypeID or ArtifactTypeGuids and PermissionType (for single-type permissions)
- ArtifactTypeID or ArtifactTypeGuids, PermissionType (for mutiple-type permissions), and Name
PermissionRef implements the IEquatable interface for permission comparison operations. Use the Equals() method with the other PermissionRef object to compare permissions. Permission comparison logic is as follows:
- Assumes that a semi-populated PermissionRef does not contain mismatched PermissionID/Name pairings.
- If PermissionID values match, then true.
- Else if the ArtifactTypeID and Name values match, then true.
- Else if the PermissionType objects match, and if the matched PermissionTypes are of a type that is expected to be single, for example, Add, Edit, or Delete, then true.
- Else if any artifact type GUIDS are specified and any of those Guids exist in both compared objects, then true.
Permission
A permission can also be represented by the Permission class, which inherits from PermissionRef. Permission is used as input when creating and updating custom permissions.
PermissionValue
The PermissionValue class inherits from PermissionRef. In addition to the inherited properties, it contains the Selected property that specifies whether the permission is enabled for a user or a group. PermissionValue is returned by the GetPermissionSelectedAsync() and GetPermissionSelectedForGroupAsync() methods of the IPermissionManager interface.
PermissionType
The PermissionType class represents the type of Relativity permission returned as the PermissionType property of PermissionRef, Permission, or PermissionValue.
PermissionType contains the following fields:
| Name | ID | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Add | 6 | Permission to add objects of a given type. |
| AdminOperations | 10 | Admin operations permission type. |
| Browser | 9 | Browser permission type. |
| Custom | 11 | Custom permission type. |
| Delete | 3 | Delete permission type. |
| Edit | 2 | Edit permission type. |
| Manage | 5 | Manage permission type. |
| MassAction | 8 | Mass action permission type. |
| Other | 7 | Other permission type. |
| Secure | 4 | Permission to set security for objects of a given type. |
| Unknown | 0 | Unknown permission type. |
| View | 1 | Permission to view objects of a given type. |
The fields can be used to reference permission type values. Here is how you would check for an Add permission type.
if(somePermissionType.Equals(PermissionType.Add)PermissionType provides the IsMultiplePermissionType() and IsSinglePermissionType() helper methods to quickly determine if a permission type is for a single or multiple.
- Single permission types are permissions to interact with objects, for example View, Add, Delete, and Secure.
- Multiple permission types are PermissionTypes that can define multiple permissions for a given object, for example Other, MassAction, Browser, AdminOperations, Custom.
You can use these constructors to initialize a PermissionType:
- PermissionType() Initializes the ID and Name to the Unknown values.
- PermissionType(int typeID) Initializes the ID and Name values to those that match the PermissionTypeID passed in, for example, 1 sets ID = 1 and Name = "View."
You can also set the PermissionType using the static PermissionType constants, for example, PermissionType.View or PermissionType.Custom.
Query permissions
You can query permissions using the QueryAsync() and QuerySubsetAsync() methods of the IPermissionManager interface. Input parameters include the workspace ArtfactID, the Query object, and optional query length. To query for admin permissions, specify -1 as the workspace ArtifactID. The resulting PermissionQueryResultSet contains a collection of Permission objects.
To query permissions:
- Create a new instance of the Query object.
- Define the search length. This is the number of results to be returned. If more results are available the search results will contain a query token that can be used with QuerySubsetAsync to get the additional results from the search query. Setting length to 0 will use the default length defined in Relativity. When the length parameter is not specified, its value defaults to 0, and the number of returned results defaults to the Instance setting table value of PDVDefaultQueryCacheSize of 10000.
- Define the search condition for the query. Conditions can be created programmatically using the Condition object and converted to a query string using the ToQueryString extension method that the query conditions accepts. The following code sample illustrates how to query for View permissions.
- Create an instance of a Sort and define how this query is to be sorted.
- Query for search objects given the above query condition and sort order. If a QueryToken is returned, more results are available that specified by the length parameter.
public static async Task QueryPermissions(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId)
{
// Create a new instance of a Query.
var query = new Relativity.Services.Query();
// Define the search length. This is the number of results to be returned.
// If more results are available the search results will contain a query
// token that can be used with QuerySubsetAsync to get the additional
// results from the search query. Setting length to 0 will use the default
// length defined in Relativity.
int length = 25;
// Define the search condition for the query. This condition
// filters for the permissions that are the View type.
// You can specify the condition syntax as a string yourself, but
// the Condition class can facilitate the construction of the queries.
var queryCondition =
new Relativity.Services.TextCondition(
Relativity.Services.PermissionFieldNames.PermissionType,
Relativity.Services.TextConditionEnum.EqualTo,
Relativity.Services.Permission.PermissionType.View.Name);
query.Condition = queryCondition.ToQueryString();
// Optional: add sorting
Relativity.Services.Sort sortBy = new Relativity.Services.Sort();
sortBy.FieldIdentifier.Name = Relativity.Services.PermissionFieldNames.PermissionID;
sortBy.Order = 0;
sortBy.Direction = Relativity.Services.SortEnum.Descending;
query.Sorts.Add(sortBy);
// Query for permissions given the above query condition and sort order.
Relativity.Services.Permission.PermissionQueryResultSet resultSet =
resultSet = await mgr.QueryAsync(workspaceId, query, length);
// This is a static method that prints out the results to
// a console window.
HandleResultSet(resultSet);
// Keep track of global starting index.
int startIndex = length + 1;
// Keep track of whether or not the resultSet is the last page.
bool onLastPage = String.IsNullOrEmpty(resultSet.QueryToken);
while (!onLastPage)
{
resultSet = await mgr.QuerySubsetAsync(
workspaceId, resultSet.QueryToken, startIndex, length);
HandleResultSet(resultSet);
onLastPage = String.IsNullOrEmpty(resultSet.QueryToken);
// Shift the starting position.
startIndex += length;
}
}The following code illustrates the HandleResultSet() method, which acts as a helper method for displaying code in the console.
private static void HandleResultSet(Relativity.Services.Permission.PermissionQueryResultSet resultSet)
{
foreach (Result<Permission> result in resultSet.Results)
{
if (result.Success)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Permission ID: {result.Artifact.PermissionID}");
Console.WriteLine($"Permission Name: {result.Artifact.Name}");
Console.WriteLine("---");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {result.Message}");
}
}
}Read a permission
You can read a single permission using the ReadSingleAsync() method of the IPermissionManager interface. Inputs include the workspace ArtifactID and a PermissionID. To read an admin permissions, specify -1 as the workspace ArtifactID.
If you do not have the permissions to view the artifact or the artifact ID is invalid, the read operation throws the following error: "ArtifactID {0} is invalid."
The following code sample illustrates how to read a permission for a document object.
public static async Task ReadSinglePermissionAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int permissionId)
{
PermissionRef permission = await mgr.ReadSingleAsync(workspaceId, permissionId);
if (permission != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {permission.Name}, ID: {permission.PermissionID}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid operation.");
}
}Some permissions can be defined because they are statically known types. The Add permission of a Document can be defined as a PermissionRef by specifying ArtifactType.ID = ArtifactType.Document and PermissionType = PermissionType.Add.
Only single type permissions for known ArtifactTypes can be defined this way.
Read the current user and group permission values
You can read the specified permissions for the current user or a specified group using the GetPermissionSelectedAsync() and GetPermissionSelectedGroupAsync() methods of the IPermissionManager interface. The methods return a list of PermissionValue objects. A PermissionValue is a fully-populated PermissionRef with an extra property Selected which will be True if the permission is enabled for the user or group.
The methods throw an error if any item in the PermissionRef list is invalid. Invalid conditions include:
- PermissionRef ID is correct but the Name is not and vice versa.
- PermissionRef ID does not exist in the system.
- PermissionRef Name does not exist in the system.
GetPermissionSelectedAsync()
The GetPermissionSelectedAsync() method returns a collection of permission values for the current user. Inputs include the workspace ArtifactID, a collection of PermissionRef objects, and an ArtifactID. To return admin permissions, specify -1 as the workspace ArtifactID. To return permissions of an item with security enabled, specify the item's ArtifactID.
GetPermissionSelectedListAsync()
The GetPermissionSelectedListAsync() method returns a collection of permission values for the current user. It is similar to GetPermissionSelectedAsync(), but instead of only returning permissions for one artifact, you can pass in a list of ArtifactIDs to return a dictionary that maps the ArtifactID to the permissions. Inputs include the workspace ArtifactID, a collection of PermissionRef objects, and a collection of ArtifactIDs. To return admin permissions, specify -1 as the workspace ArtifactID.
public static async Task GetSelectedPermissionListAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, List<int> artifactIds)
{
// GUID for document object type
Guid documentTypeGuid = new Guid("15C36703-74EA-4FF8-9DFB-AD30ECE7530D");
var permissions = new List<Relativity.Services.Permission.PermissionRef>
{
new PermissionRef
{
// Redact Document
PermissionID = 1000006
},
new PermissionRef
{
// Permissions can also be identified by an ArtifactType ID/Guid and a Name
ArtifactType = new Relativity.Services.ArtifactTypeIdentifier(documentTypeGuid),
Name = "Replace Document"
}
};
Dictionary<int, List<PermissionValue>> permissionValues =
await mgr.GetPermissionSelectedListAsync(workspaceId, permissions, artifactIds);
foreach (KeyValuePair<int, List<PermissionValue>> permissionVal in permissionValues)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Permissions for object {permissionVal.Key}");
// Get the list of permissions associated with the object
List<PermissionValue> permissionVals = permissionVal.Value;
// Print out the value of each permission
permissionVals
.ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine($"{x.Name} selected: {x.Selected}"));
}
}GetPermissionSelectedGroupAsync()
The GetPermissionSelectedGroupAsync() method returns a collection of permission values for the specified group. Inputs include the workspace ArtifactID, a collection of PermissionRef objects, and a GroupRef object. To return admin permissions, specify -1 as the workspace ArtifactID. To return permission values of an item with security enabled, specify the item's artifact ID.
public static async Task GetPermissionsForGroup(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int groupId)
{
// Wrap the group artifact ID inside a GroupRef object
var groupRef = new GroupRef(groupId);
// GUID for Production object type
Guid productionTypeGuid = new Guid("24190650-2E73-4373-B0C4-F31142CBF300");
var permissions = new List<Relativity.Services.Permission.PermissionRef>
{
new PermissionRef
{
// Mass Edit
PermissionID = 1000001
},
new PermissionRef
{
// Permissions can also be identified by an ArtifactType ID/Guid and a Name
ArtifactType = new Relativity.Services.ArtifactTypeIdentifier(productionTypeGuid),
Name = "Secure Production"
}
};
List<PermissionValue> permissionValues =
await mgr.GetPermissionSelectedForGroupAsync(workspaceId, permissions, groupRef);
// Print out the values for each permission
permissionValues
.ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine($"{x.Name} selected: {x.Selected}"));
}Set permission values
You can set individual permissions for a specified group using the SetPermissionSelectedforGroupAsync() method of the IPermissionManager interface. Inputs include the workspace ArtifactID, a collection of PermissionValue objects, and a GroupRef object. To set admin permissions, specify -1 as the workspace ArtifactID. To set permissions for an item with security enabled, specify the item's artifact ID.
public static async Task SetPermissionsForGroupAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int groupId)
{
// Wrap the group artifact ID inside a GroupRef object
var groupRef = new GroupRef(groupId);
// Specify list of permissions to update
var permissionValues = new List<PermissionValue>
{
new PermissionValue
{
// Edit View
PermissionID = 24,
Selected = true
}
};
await mgr.SetPermissionSelectedForGroupAsync(workspaceId, permissionValues, groupRef);
Console.WriteLine("Success.");
}Custom permissions
You can define custom permissions for Relativity Dynamic Objects (RDOs). Relativity Legal Hold is an example of an application that uses RDOs with custom permissions, such as Acknowledge on Behalf, Escalate, and Remind.
The Services API supports the create, update, delete, and query operations on Permission DTOs for managing custom permissions. Note that the all other operations that can be performed on Relativity system permissions using the IPermissionManager interface can also be performed on custom permissions. For code samples of reading and querying permissions, see Work with individual permissions.
Create a permission
The following code sample illustrates how to create a custom permission. Note the use of the Permission class to instantiate the new permission. The ArtifactType.ID property is set to the artifact type ID of the RDO for which the custom permission is created. Also note the use of the PermissionType class to set the PermissionType property to custom.
public static async Task<int> CreateSinglePermissionAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int rdoTypeId)
{
var permission = new Permission
{
Name = "My Custom Permission",
PermissionType = PermissionType.Custom,
ArtifactType = new ArtifactTypeIdentifier(rdoTypeId)
};
int createdPermissionId = await mgr.CreateSingleAsync(workspaceId, permission);
Console.WriteLine($"Successfully created permission with ID {createdPermissionId}.");
return createdPermissionId;
}Read a permission
You can read a single permission using the ReadSingleAsync() method of the IPermissionManager interface. Inputs include the workspace ArtifactID and a PermissionID. To read an admin permissions, specify -1 as the workspace ArtifactID. The following code sample illustrates how to read a permission for a document object.
public static async Task ReadSinglePermissionAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int permissionId)
{
PermissionRef permission = await mgr.ReadSingleAsync(workspaceId, permissionId);
if (permission != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {permission.Name}, ID: {permission.PermissionID}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid operation.");
}
}Some permissions can be defined because they are statically known types. The Add permission of a Document can be defined as a PermissionRef by specifying ArtifactType.ID = ArtifactType.Document and PermissionType = PermissionType.Add.
Only single type permissions for known ArtifactTypes can be defined this way.
Update a permission
The following code sample illustrates how to update a custom permission.
public static async Task UpdateSinglePermissionAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int permissionId)
{
var updated = new Relativity.Services.Permission.Permission
{
PermissionID = permissionId,
Name = "New Permission Name"
};
await mgr.UpdateSingleAsync(workspaceId, updated);
Console.WriteLine("Success.");
}Delete a permission
The following code sample illustrates how to delete a custom permission.
public static async Task DeleteSinglePermissionAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int permissionId)
{
await mgr.DeleteSingleAsync(workspaceId, permissionId);
Console.WriteLine($"Successfully deleted permission {permissionId}.");
}Add and remove groups to permissions
Before specific permissions can be assigned, a group must be added to admin, workspace, or item permissions.
Groups with assigned admin, workspace, or item permissions are represented by the GroupSelector class. The groups with permissions are listed as a collection of GroupRef objects in the EnabledGroups property. All other groups in the Relativity instance are listed in the DisabledGroup property.
Admin groups
To return an instance of GroupSelector for admin permissions, use the GetAdminGroupSelector() method of the Permission interface.
GroupSelector selector = await proxy.GetAdminGroupSelectorAsync();This is equivalent to displaying groups with admin permissions in the Admin Security dialog (accessed from the Instance Details tab).
public static async Task ReadAdminGroupsAsync(IPermissionManager mgr)
{
GroupSelector sel = await mgr.GetAdminGroupSelectorAsync();
// local function to print out group info
void printGroup(GroupRef x) => Console.WriteLine($"{x.ArtifactID} ({x.Name})");
Console.WriteLine("Enabled:");
sel.EnabledGroups.ForEach(printGroup);
Console.WriteLine("Disabled:");
sel.DisabledGroups.ForEach(printGroup);
}To add and remove groups to admin permissions:
- Get a GroupSelector as shown above.
- After you have a GroupSelector, manipulate the GroupSelector by moving the groups into the EnabledGroups and DisabledGroups collections as GroupRef objects. (For simplicity you can set the enabled and disabled groups to only the groups you wish to modify. All other groups will not be altered within the GroupSelector object when setting the values.)Copy
List<GroupRef> groupRefs = new List<GroupRef>() {new GroupRef(groupID.Value)};
// Add a group.
adminSelector.EnabledGroups = groupRefs;
adminSelector.DisabledGroups = new List<GroupRef>(); - Set the groups by calling the AddRemoveAdminGroupsAsync() method of the Permission interface and pass in the GroupSelector object.Copy
await proxy.AddRemoveAdminGroupsAsync(adminSelector);
The GroupSelector object must have the latest value of LastModified, and every call that returns GroupSelector will update this value. This prevents a user from reading a value and modifying it if another user has read that value with the intent of changing it as well. Item-level security must be enabled to add or remove groups to the permissions for individual items.
public static async Task AddRemoveGroupFromAdminAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, List<int> toAdd, List<int> toRemove)
{
// Remove duplicates from the toAdd list
HashSet<int> remove = new HashSet<int>(toRemove);
List<int> toAddClean = toAdd.Where(x => !(remove.Contains(x))).ToList();
// Wrap the items in a GroupRef object
List<GroupRef> toAddRefs = toAddClean.Select(x => new GroupRef(x)).ToList();
List<GroupRef> toRemoveRefs = toRemove.Select(x => new GroupRef(x)).ToList();
// Get current enabled/disabled groups
GroupSelector sel = await mgr.GetAdminGroupSelectorAsync();
// Add/remove groups
sel.EnabledGroups = toAddRefs;
sel.DisabledGroups = toRemoveRefs;
// Push changes
await mgr.AddRemoveAdminGroupsAsync(sel);
}Workspace groups
To return an instance of GroupSelector for a workspace, use the GetWorkspaceGroupSelector() method of the Permission interface and pass in the workspace Artifact ID.
GroupSelector selector = await proxy.GetWorkspaceGroupSelectorAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID);This is equivalent to displaying groups with workspace permissions in the Workspace Security dialog (accessed from the Workspace Details tab).
public static async Task ReadGroupsInWorkspaceAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId)
{
GroupSelector sel = await mgr.GetWorkspaceGroupSelectorAsync(workspaceId);
Console.WriteLine("Enabled groups:");
sel.EnabledGroups.ForEach(grp => Console.WriteLine(grp.Name));
Console.WriteLine("------");
Console.WriteLine("Disabled Groups:");
sel.DisabledGroups.ForEach(grp => Console.WriteLine(grp.Name));
}To add and remove groups to workspace permissions:
- Get a GroupSelector as shown above.
- After you have a GroupSelector, manipulate the GroupSelector by moving the groups into the EnabledGroups and DisabledGroups collections as GroupRef objects. (For simplicity you can set the enabled and disabled groups to only the groups you wish to modify. All other groups will not be altered within the GroupSelector object when setting the values.)Copy
List<GroupRef> groupRefs = new List<GroupRef>() {new GroupRef(groupID.Value)};
// Add a group.
adminSelector.EnabledGroups = groupRefs;
adminSelector.DisabledGroups = new List<GroupRef>(); - Set the groups by calling the AddRemoveWorkspaceGroupsAsync() method of the Permission interface and pass in the GroupSelector object.Copy
await proxy.AddRemoveWorkspaceGroupsAsync(workspaceSelector);
public static async Task AddRemoveGroupsFromWorkspace(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, List<int> toAdd, List<int> toRemove)
{
// Remove duplicates from the toAdd list
HashSet<int> remove = new HashSet<int>(toRemove);
List<int> toAddClean = toAdd.Where(x => !(remove.Contains(x))).ToList();
// Wrap the items in a GroupRef object
List<GroupRef> toAddRefs = toAddClean.Select(x => new GroupRef(x)).ToList();
List<GroupRef> toRemoveRefs = toRemove.Select(x => new GroupRef(x)).ToList();
// Get current enabled/disabled groups
GroupSelector sel = await mgr.GetWorkspaceGroupSelectorAsync(workspaceId);
// Add/remove groups
sel.EnabledGroups = toAddRefs;
sel.DisabledGroups = toRemoveRefs;
// Push changes
await mgr.AddRemoveWorkspaceGroupsAsync(workspaceId, sel);
}Item groups
To return an instance of GroupSelector for an admin or workspace item, use the GetItemGroupSelector() method of the Permission interface and pass in the Artifact IDs of the workspace and the item.
GroupSelector selector = await proxy.GetItemGroupSelectorAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, this.SampleRDO_ID);This is equivalent to displaying groups with item permissions in the Item Security dialog (accessed by clicking the Security icon ( ) for an item in the list).
) for an item in the list).
public static async Task ReadGroupAccessForItem(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int artifactId)
{
GroupSelector sel = await mgr.GetItemGroupSelectorAsync(workspaceId, artifactId);
// Local function to print out group info
void printGroup(GroupRef x) => Console.WriteLine($"{x.ArtifactID} ({x.Name})");
Console.WriteLine("Enabled:");
sel.EnabledGroups.ForEach(printGroup);
Console.WriteLine("Disabled:");
sel.DisabledGroups.ForEach(printGroup);
}To add and remove groups to item permissions:
- Get a GroupSelector as shown above.
- After you have a GroupSelector, manipulate the GroupSelector by moving the groups into the EnabledGroups and DisabledGroups collections as GroupRef objects. (For simplicity you can set the enabled and disabled groups to only the groups you wish to modify. All other groups will not be altered within the GroupSelector object when setting the values.)Copy
List<GroupRef> groupRefs = new List<GroupRef>() {new GroupRef(groupID.Value)};
// Add a group.
adminSelector.EnabledGroups = groupRefs;
adminSelector.DisabledGroups = new List<GroupRef>(); - Set the groups by calling the AddRemoveItemGroupsAsync() method of the Permission interface and pass in the GroupSelector object.Copy
await proxy.AddRemoveItemGroupsAsync(itemSelector);
public static async Task SecureItemFromGroup(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int artifactId)
{
// Name of group from which to secure item
const string groupName = "First Level Group";
// First enable item-level security
ItemLevelSecurity itemLevelSecurity =
await mgr.GetItemLevelSecurityAsync(workspaceId, artifactId);
if (!itemLevelSecurity.Enabled)
{
itemLevelSecurity.Enabled = true;
await mgr.SetItemLevelSecurityAsync(workspaceId, itemLevelSecurity);
}
// Get enabled and disabled groups for a particular document
GroupSelector sel = await mgr.GetItemGroupSelectorAsync(workspaceId, artifactId);
foreach (GroupRef group in sel.EnabledGroups)
{
if (group.Name == groupName)
{
sel.DisabledGroups.Add(group);
sel.EnabledGroups.Remove(group);
Console.WriteLine($"Securing item {artifactId} from {group.Name}.");
await mgr.AddRemoveItemGroupsAsync(workspaceId, artifactId, sel);
Console.WriteLine("Successfully secured item!");
break;
}
}
}Enable item-level security
In order to set item permissions, Item-level security must be enabled for individual Relativity artifacts. Item-level security is represented by the ItemLevelSecurity class.
ItemLevelSecurity class includes the following properties:
- ArtifactID – ArtifactID.
- Enabled – Is Item Level Security enabled.
- LastModified – Last modified timestamp.
Get item-level security
To return item-level security settings for a Relativity artifact, use the GetItemLevelSecurityAsync() and GetItemLevelSecurityListAsync() methods of the Permission interface.
GetItemLevelSecurityAsync()
The GetItemLevelSecurityAsync() method returns the item-level security settings for a specified workspace and the artifact ID.
ItemLevelSecurity itemLevelSecurity = await proxy.GetItemLevelSecurityAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, this.SampleRDO_ID);
int id = itemLevelSecurity.ArtifactID;
bool enabled = itemLevelSecurity.Enabled;
DateTime lastModified = itemLevelSecurity.LastModified;
string info = string.Format("{0} : {1} - {2}", id, enabled, lastModified);Complete code sample
public static async Task<bool> IsItemLevelSecurityEnabled(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int artifactId)
{
ItemLevelSecurity itemLevelSecurity =
await mgr.GetItemLevelSecurityAsync(workspaceId, artifactId);
return itemLevelSecurity.Enabled;
}GetItemLevelSecurityListAsync()
The GetItemLevelSecurityListAsync() method is similar to GetItemLevelSecurityAsync(), but instead of returning item-level security for one artifact, you can pass in a list of ArtifactIDs and return a dictionary.
Dictionary<int, ItemLevelSecurity> itemLevelSecurity = await proxy.GetItemLevelSecurityListAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, new List<int> { this.SampleRDO_ID } );
//GetItemLevelSecurityListAsync returns a dictionary
//Key is the item's ArtifactID
//and value contains the item's ArtifactID, whether item level security is enabled, and when the security was last modified
int id = itemLevelSecurity[this.SampleRDO_ID].ArtifactID;
bool enabled = itemLevelSecurity[this.SampleRDO_ID].Enabled;
DateTime lastModified = itemLevelSecurity[this.SampleRDO_ID].LastModified;
string info = string.Format("{0} : {1} - {2}", id, enabled, lastModified);
//If the user making the request does not have secure permissions on the item they'll get back an empty object
this.Logger.LogMessage(Client.SamplesLibrary.Logging.LogLevel.Debug, new StackFrame(0).GetMethod().Name, info, this.GetType().Name);
success = true;Complete code sample
public static async Task ReadItemLevelSecurityListAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, List<int> artifactIds)
{
Dictionary<int, ItemLevelSecurity> dict =
await mgr.GetItemLevelSecurityListAsync(workspaceId, artifactIds);
// Loop through the artifact IDs and print whether or not
// its item-level security is enabled
artifactIds.ForEach(item => Console.WriteLine($"{item}: {dict[item].Enabled}"));
}Set item-level security
To enable or disable item-level security settings for a Relativity artifact, use the SetItemLevelSecurityAsync() method of the Permission interface and pass in the Artifact IDs of the workspace and the artifact.
ItemLevelSecurity itemLevelSecurity = await proxy.GetItemLevelSecurityAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, this.SampleRDO_ID);
itemLevelSecurity.Enabled = !itemLevelSecurity.Enabled;
await proxy.SetItemLevelSecurityAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, itemLevelSecurity);After item level security is enabled, you can set item-level permissions.
Complete code sample
public static async Task EnableItemLevelSecurity(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int artifactId)
{
ItemLevelSecurity itemLevelSecurity =
await mgr.GetItemLevelSecurityAsync(workspaceId, artifactId);
itemLevelSecurity.Enabled = true;
await mgr.SetItemLevelSecurityAsync(workspaceId, itemLevelSecurity);
Console.WriteLine($"Successfully enabled item-level security for {artifactId}")
}Set group permissions
After groups have been added, you can assign them specific admin, workspace, or item permissions.
Group permissions are represented by the GroupPermissions class. GroupPermissions contains these properties corresponding to the Relativity permissions categories:
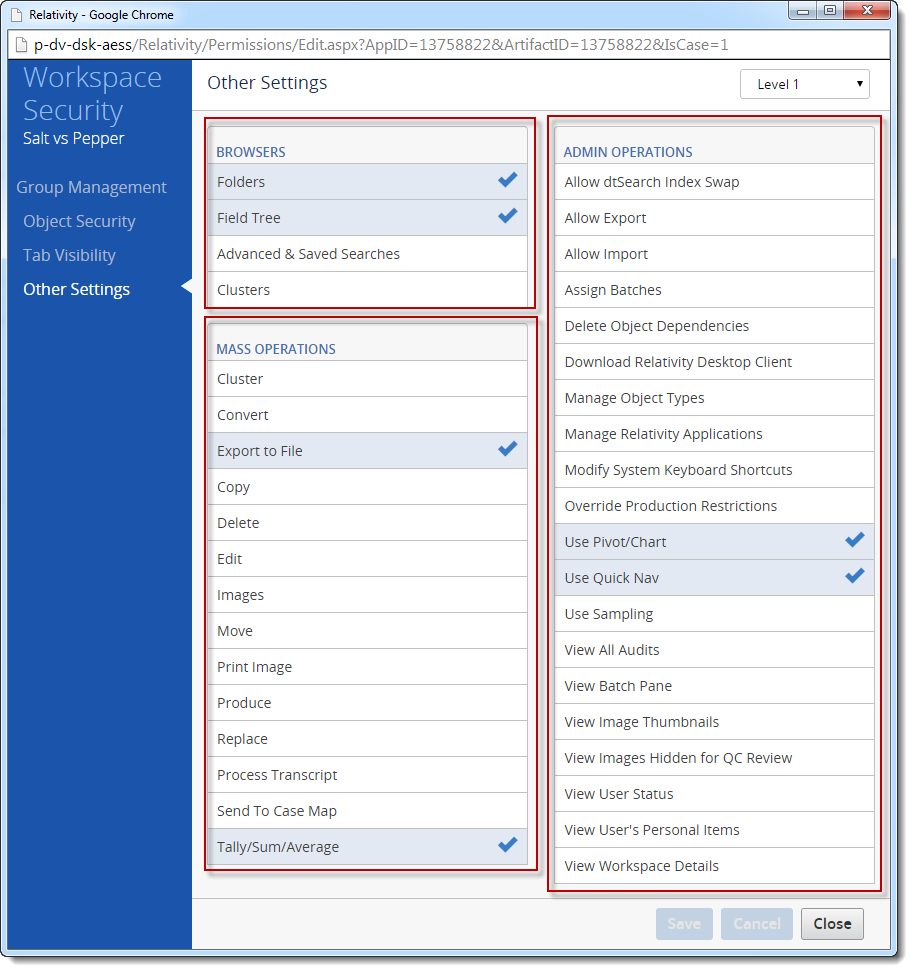
- AdminPermissions – Admin permissions. Different admin permissions can be set on the admin and workspace level. The property is a collection of GenericPermission objects.
- BrowserPermissions – Relativity user interface browser permissions set on the workspace level. The property is a collection of GenericPermission objects.
- MassActionPermissions – Mass action permissions set on the workspace level. The property is a collection of GenericPermission objects.
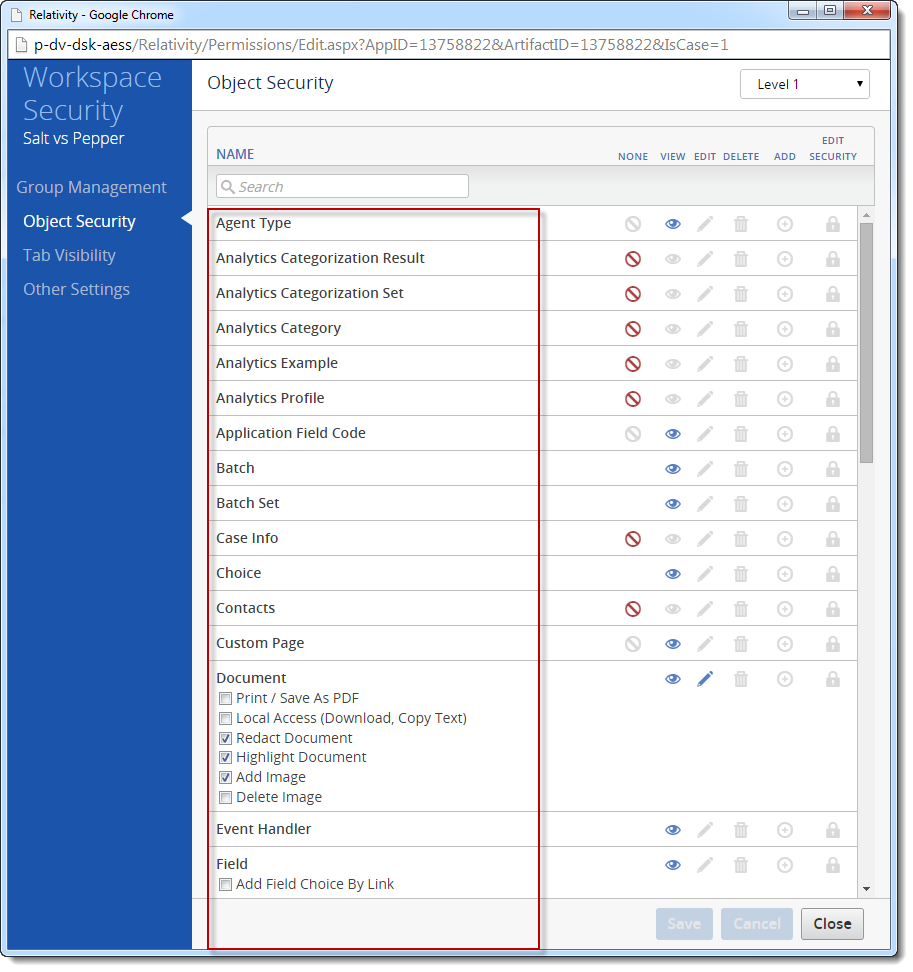
- ObjectPermissions – Object permissions. Different object permissions can be set on the admin, workspace, and item level. The property is a collection of ObjectPermission objects.
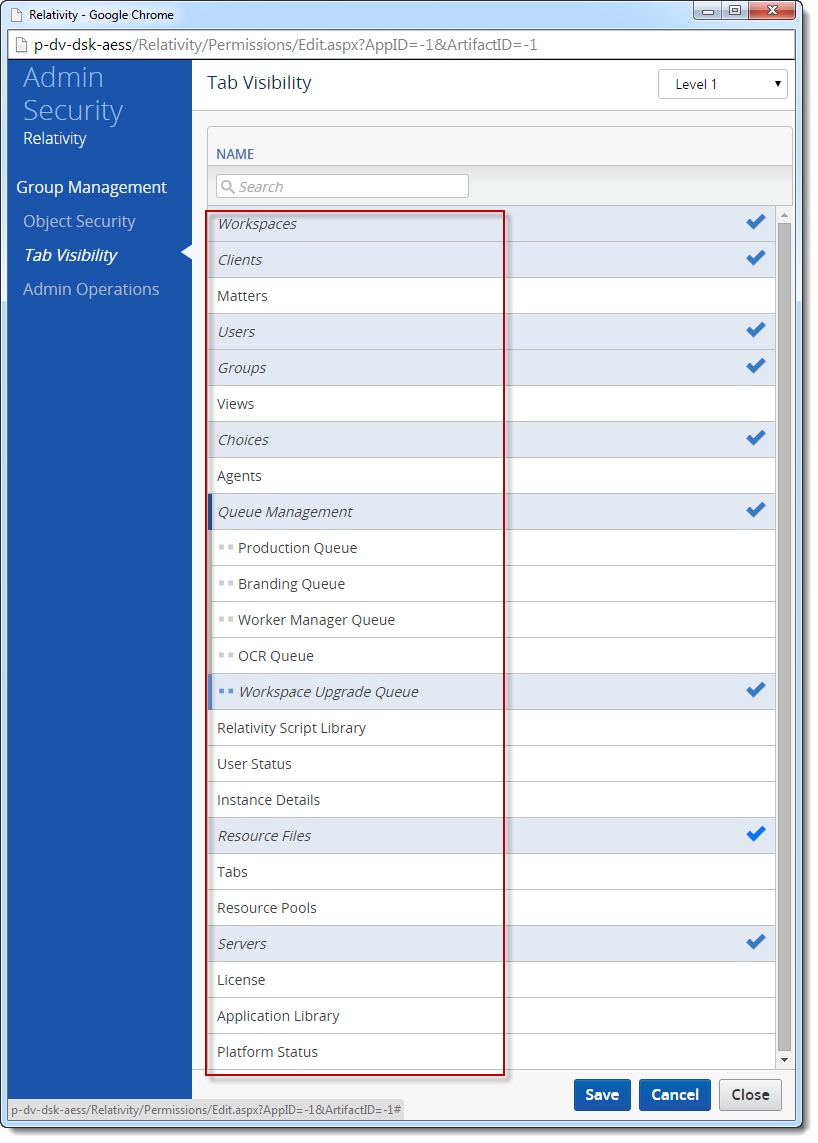
- TabVisibility – Tab visibility. The property is a collection of ObjectPermission objects.
ObjectPermission class includes these properties:
- AddEditable – Indicates whether the group can modify add permissions.
- AddSelected -Indicates whether the group has add permissions.
- ArtifactGroupingID – The ID that links the permission to the group.
- ArtifactTypeID – ArtifactTypeID of the object.
- CanRemovePermissions – Indicates whether the group can disable all permissions.
- CustomPermissions – Custom permission details.
- DeleteEditable – Indicates whether the group can modify delete permissions.
- DeleteSelected – Indicates whether the group has delete permission.
- EditEditable – Indicates whether the group can modify edit permissions.
- EditSecurityEditable – Indicates whether the group can modify EditSecurity permissions.
- EditSecuritySelected – Indicates whether the group has EditSecurity permission.
- EditSelected – Indicates whether the group has Edit permission.
- HasChildPermissions – Indicates if this has child permissions.
- HierarchyIndent – Indicates the current indent of this permission hierarchy.
- Name – Permission display name.
- ParentArtifactTypeID – Parent ArtifactTypeID.
- SubPermissions – Subpermission details. The property is a collection of PermissionDetail objects.
- ViewSelected – Indicates whether view permissions are enabled.
GenericPermission class represent non-object permissions. The class includes these properties:
- Children – Generic permission child permissions.
- Editable – Generic permission can be modified.
- Name – Generic permission name.
- Selected – Generic permission type is selected.
- Value – ArtifactID.
Subpermissions are represented by the PermissionDetail class. PermissionDetail includes these properties:
- Name – Permission name
- PermissionID – Permission ID.
- Selected – Permission of given type is selected.
To modify individual permissions without reading all group permissions, use the SetPermissionSelectedForGroupAsync() method. For more information, see Set permission values.
Admin group permissions
IPermissionManager interface provides the methods to get and set the admin group permissions.
Get admin group permissions
To return an instance of admin GroupPermissions, use the GetAdminGroupPermissionsAsync() method of the IPermissionManager interface.
GroupPermissions permissions = await proxy.GetAdminGroupPermissionsAsync(groupRef);The resulting GroupPermissions objects contains the following admin permissions.
Complete code sample
public static async Task GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int groupId)
{
// Get the current workspace permissions for the group
GroupPermissions permissions =
await mgr.GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(workspaceId, new GroupRef(groupId));
// The Group Permissions object returns a lot of information such as
// the Artifact ID of the permission, the group ID, and the last time
// the permissions were modified
string info = String.Format("Permissions ID: {0} - Group ID: {1} : {2}",
permissions.ArtifactID,
permissions.GroupID,
permissions.LastModified);
Console.WriteLine(info);
// GroupPermissions contains lists of GenericPermission objects for
// admin permissions, browser permissions, mass action permissions,
// and tab visibility
permissions.TabVisibility
.ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine($"{x.Name} selected: {x.Selected} editable: {x.Editable}"));
// The other list of permissions that GroupPermissions contains is
// ObjectPermissions
foreach (ObjectPermission permission in permissions.ObjectPermissions)
{
// Indicates if group members can change the "Add" permission
bool canChangeAddPermission = permission.AddEditable;
// Indicates if group members can "Add" the given object
bool canAdd = permission.AddSelected;
// ObjectPermission also contains permission hierarchy information when applicable:
// bool childPermissions = permission.HasChildPermissions;
// int hierarchyIndent = permission.HierarchyIndent;
// int parentArtifactTypeID = permission.ParentArtifactTypeID;
// List<PermissionDetail> permissionDetails = permission.SubPermissions;
info = string.Format("Type: {0} - Name: {1}",
permission.ArtifactTypeID, permission.Name);
Console.WriteLine(info);
}
}Set admin group permissions
To set admin group permissions:
- Get the full permission structure in the GroupPermissions objects by calling GetAdminGroupPermissionsAsync() method of the Permissions interface.Copy
GroupPermissions permissions = await proxy.GetAdminGroupPermissionsAsync(groupRef); - After you return a current GroupPermissions object, you can then inspect and manipulate the permissions within the object.Copy
List<ObjectPermission> objectPermissions = permissions.ObjectPermissions;
ObjectPermission objectPermission = objectPermissions.First(x => x.Name == "Some Permission Name");
objectPermission.EditSecuritySelected = false;permissions.TabVisibility = tabVisibility; - After setting the permissions, pass the GroupPermissions object to the SetAdminGroupPermissionsAsync() of the Permissions interface. Copy
await proxy.SetAdminGroupPermissionsAsync(permissions);
The GroupPermissions object must have the latest value of LastModified, and every call that returns GroupPermissions will update this value. This prevents a user from reading a value and modifying it if another user has read that value with the intent of changing it as well. Item-level security must be enabled to change item-level permissions.
Complete code sample
public static async Task SetAdminGroupsAccessAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int groupId)
{
// Wrap the group ID inside a GroupRef object
var groupRef = new GroupRef(groupId);
// Get the group's current permissions.
// It is easier to read the full permission structure back because
// needs to be passed back to set permissions even if there were no
// changes to the permissions
Relativity.Services.Permission.GroupPermissions permissions =
await mgr.GetAdminGroupPermissionsAsync(groupRef);
// Get the current tab visibility
List<Relativity.Services.Permission.GenericPermission> tabVisibility =
permissions.TabVisibility;
// Find the index of the tab visibility permission for "Matters"
int matterIndex = tabVisibility.FindIndex(x => x.Name == "Matters");
// There are two fields that change permissions in a GenericPermission object:
// Editable is a read only param that specifies if a user can or
// cannot edit the permission
// Selected is the permission itself, in this case we're setting the
// tab to not show for this group
tabVisibility[matterIndex].Selected = false;
// It is also possible to get the ArtifactID from the current permission object:
// tabVisibility[matterIndex].Value;
// There is also a structure for Child permissions which is just another
// list of Generic Permissions and is accessed like so:
// tabVisibility[matterIndex].Children;
permissions.TabVisibility = tabVisibility;
await mgr.SetAdminGroupPermissionsAsync(permissions);
}Workspace group permissions
IPermissionManager interface provides the methods to get and set the workspace permissions for groups.
Get workspace group permissions
To return an instance of workspace GroupPermissions, use the GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync() method of the Permission interface and pass in the Artifact IDs of the workspace.
GroupPermissions permissions = await proxy.GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, groupRef);The resulting GroupPermissions object contains the following workspace permissions.
Complete code sample
public static async Task GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int groupId)
{
// Get the current workspace permissions for the group
GroupPermissions permissions =
await mgr.GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(workspaceId, new GroupRef(groupId));
// The Group Permissions object returns a lot of information such as
// the Artifact ID of the permission, the group ID, and the last time
// the permissions were modified
string info = String.Format("Permissions ID: {0} - Group ID: {1} : {2}",
permissions.ArtifactID,
permissions.GroupID,
permissions.LastModified);
Console.WriteLine(info);
// GroupPermissions contains lists of GenericPermission objects for
// admin permissions, browser permissions, mass action permissions,
// and tab visibility
permissions.TabVisibility
.ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine($"{x.Name} selected: {x.Selected} editable: {x.Editable}"));
// The other list of permissions that GroupPermissions contains is
// ObjectPermissions
foreach (ObjectPermission permission in permissions.ObjectPermissions)
{
// Indicates if group members can change the "Add" permission
bool canChangeAddPermission = permission.AddEditable;
// Indicates if group members can "Add" the given object
bool canAdd = permission.AddSelected;
// ObjectPermission also contains permission hierarchy information when applicable:
// bool childPermissions = permission.HasChildPermissions;
// int hierarchyIndent = permission.HierarchyIndent;
// int parentArtifactTypeID = permission.ParentArtifactTypeID;
// List<PermissionDetail> permissionDetails = permission.SubPermissions;
info = string.Format("Type: {0} - Name: {1}",
permission.ArtifactTypeID, permission.Name);
Console.WriteLine(info);
}
}Set workspace group permissions
To set workspace group permissions:
- Get the full permission structure in the GroupPermissions objects by calling GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync() method of the Permissions interface.Copy
GroupPermissions permissions = await proxy.GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(groupRef); - After you return a current GroupPermissions object, you can then inspect and manipulate the permissions within the object.Copy
List<ObjectPermission> objectPermissions = permissions.ObjectPermissions;
ObjectPermission objectPermission = objectPermissions.First(x => x.Name == "Some Permission Name");
objectPermission.EditSecuritySelected = false;permissions.TabVisibility = tabVisibility; - After setting the permissions, pass the GroupPermissions object to the SetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync() of the Permissions interface. Copy
await proxy.SetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(permissions);
The GroupPermissions object must have the latest value of LastModified, and every call that returns GroupPermissions will update this value. This prevents a user from reading a value and modifying it if another user has read that value with the intent of changing it as well. Item-level security must be enabled to change item-level permissions.
Complete code sample
public static async Task SetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int groupId)
{
GroupRef groupRef = new GroupRef(groupId);
// Get the permissions associated with said group
GroupPermissions permissions = await mgr.GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(workspaceId, groupRef);
// Print out Object Permissions
Console.WriteLine("Permissions for members of {0} BEFORE", groupRef.ArtifactID);
foreach (ObjectPermission objPerm in permissions.ObjectPermissions)
{
Console.WriteLine("Object Name: {0}", objPerm.Name);
// we could print out others, but let's just print out if group
// members can add a given object (true/false)
Console.WriteLine("Can Add: {0}", objPerm.AddSelected);
// Set the "Add" permission to false
objPerm.AddSelected = false;
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Apply changes
await mgr.SetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(workspaceId, permissions);
// Read back to see if changes have applied
permissions = await mgr.GetWorkspaceGroupPermissionsAsync(workspaceId, groupRef);
Console.WriteLine("Permissions for members of {0} AFTER", groupRef.ArtifactID);
foreach (ObjectPermission objPerm in permissions.ObjectPermissions)
{
Console.WriteLine("Object Name: {0}", objPerm.Name);
Console.WriteLine("Can Add: {0}", objPerm.AddSelected);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}Item group permissions
IPermissionManager interface provides the methods to get and set group permissions for individual Relativity items.
Get item group permissions
To return an instance of item GroupPermissions, use the GetItemGroupPermissionsAsync() method of the Permission interface and pass in the Artifact IDs of the workspace and the item.
GroupPermissions permissions = await proxy.GetItemGroupPermissionsAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, this.SampleRDO_ID, groupRef);The arguments passed to the GetItemGroupPermissionsAsync() method include:
- this.SampleWorkspace_ID - the Artifact ID of the workspace where the item exists.
- this.SampleRDO_ID - the Artifact ID of the item that you want to the group permissions for.
- groupRef - a Reference object for a group, whose permissions to the item you want to find. Reference the group by name or Artifact ID.
The resulting GroupPermissions object can contain different sets of properties depending on the object type. The following is an example of Document object permissions. Note that the Subpermissions property (Print/Save As PDF, Redact, Highlight Document, etc.) contains a collection of PermissionDetail objects.
Complete code sample
public static async Task GetItemLevelGroupPermissionsAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int artifactId, int groupId)
{
var groupRef = new GroupRef(groupId);
GroupPermissions permissions =
await mgr.GetItemGroupPermissionsAsync(workspaceId, artifactId, groupRef);
// Print out the object permissions
foreach (ObjectPermission permission in permissions.ObjectPermissions)
{
// Indicates if group members can change the "Add" permission
bool canChangeAddPermission = permission.AddEditable;
// Indicates if group members can "Add" the given object
bool canAdd = permission.AddSelected;
// ObjectPermission also contains permission hierarchy information when applicable:
// bool childPermissions = permission.HasChildPermissions;
// int hierarchyIndent = permission.HierarchyIndent;
// int parentArtifactTypeID = permission.ParentArtifactTypeID;
// List<PermissionDetail> permissionDetails = permission.SubPermissions;
string info = string.Format("Artifact Type ID: {0} - Name: {1}",
permission.ArtifactTypeID, permission.Name);
Console.WriteLine(info);
}
}Set item group permissions
To set item group permissions:
- Get the full permission structure in the GroupPermissions objects by calling GetItemGroupPermissionsAsync() method of the Permissions interface.Copy
GroupPermissions permissions = await proxy.GetItemGroupPermissionsAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, this.SampleRDO_ID, groupRef);The arguments passed to the GetItemGroupPermissionsAsync() method include:
- this.SampleWorkspace_ID - the Artifact ID of the workspace where the item exists.
- this.SampleRDO_ID - the Artifact ID of the item that you want to the group permissions for.
- groupRef - a Reference object for a group, whose permissions to the item you want to find. Reference the group by name or Artifact ID.
- After you return a current GroupPermissions object, you can then inspect and manipulate the permissions within the object.Copy
List<ObjectPermission> objectPermissions = permissions.ObjectPermissions;
ObjectPermission objectPermission = objectPermissions.First(x => x.Name == "Some Permission Name");
objectPermission.EditSecuritySelected = false;
permissions.TabVisibility = tabVisibility; - After setting the permissions, pass the GroupPermissions object to the SetItemGroupPermissionsAsync() of the Permissions interface. Copy
await proxy.SetItemGroupPermissionsAsync(permissions);
The GroupPermissions object must have the latest value of LastModified, and every call that returns GroupPermissions will update this value. This prevents a user from reading a value and modifying it if another user has read that value with the intent of changing it as well. Item-level security must be enabled to change item-level permissions.
Complete code sample
public static async Task SetItemLevelGroupPermissionsAsync(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int artifactId, int groupId)
{
// Get the current permissions
GroupPermissions currPermissions =
await mgr.GetItemGroupPermissionsAsync(workspaceId, artifactId, new GroupRef(groupId));
List<ObjectPermission> objectPermissions = currPermissions.ObjectPermissions;
// If the artifact ID passed in as a parameter corresponds to
// a document, then there should only be one set of object permissions.
// Here, however, we are just ensuring that we are in the Document section anyway.
int documentIndex = objectPermissions.FindIndex(x => x.Name == "Document");
ObjectPermission documentVisibility = objectPermissions[documentIndex];
// Besides the basic View, Edit, Create, Delete, Edit Security, and Add permissions,
// there are also possibilites for sub permissions (in this case, documents).
// Those would be Print / Save as PDF, Add Image, Delete Image, etc.
documentVisibility.EditSecuritySelected = false;
// The sub-permissions are a list within the ObjectPermission
List<PermissionDetail> subPermissions = documentVisibility.SubPermissions;
int addImageIndex = subPermissions.FindIndex(x => x.Name == "Add Image");
subPermissions[addImageIndex].Selected = true;
currPermissions.ObjectPermissions = objectPermissions;
// Update the permissions
await mgr.SetItemGroupPermissionsAsync(workspaceId, currPermissions);
}User lookup in groups
The Permissions interface provides helper methods to return a list of users associated with a group with a admin, workspace, or item permissions.
Get admin group users
To return a list of users in a group with admin permissions (corresponding to the EDDS Relativity database), call the GetAdminGroupUsersAsync() and pass in the GroupRef object.
List<UserRef> users = await proxy.GetAdminGroupUsersAsync(groupRef);
foreach (UserRef userRef in users)
{
string info = string.Format("{0} : {1}", userRef.ArtifactID, userRef.Name);
}Complete code sample
public static async Task GetAdminUsersInGroup(IPermissionManager mgr, int groupId)
{
List<Relativity.Services.User.UserRef> adminUsers =
await mgr.GetAdminGroupUsersAsync(new GroupRef(groupId));
Console.WriteLine($"Admin users in group {groupId}:");
adminUsers
.ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine($"{x.ArtifactID} - {x.Name}"));
}Get workspace group users
To return a list of users in a group with workspace permissions (corresponding to a Relativity workspace database), call the GetWorkspaceGroupUsersAsync() and pass in the Artifact ID of the workspace and a GroupRef object for the group.
List<UserRef> users = await proxy.GetWorkspaceGroupUsersAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, groupRef);
foreach (UserRef userRef in users)
{
string info = string.Format("{0} : {1}", userRef.ArtifactID, userRef.Name);
}Complete code sample
public static async Task GetWorkspaceGroupUsers(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int groupId)
{
List<Relativity.Services.User.UserRef> users =
await mgr.GetWorkspaceGroupUsersAsync(workspaceId, new GroupRef(groupId));
Console.WriteLine($"Users in group {groupId} with access to workspace {workspaceId}:");
users.ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine($"{x.ArtifactID} - {x.Name}"));
}Get item group users
To return a list of users in a group with item permissions, call the GetItemGroupUsersAsync() and pass in the Artifact IDs of the workspace and the item, and a GroupRef object for the group.
List<UserRef> users = await proxy.GetAdminGroupUsersAsync(this.SampleWorkspace_ID, this.SampleDocument_ID, groupRef);
foreach (UserRef userRef in users)
{
string info = string.Format("{0} : {1}", userRef.ArtifactID, userRef.Name);
}Complete code sample
public static async Task GetItemGroupUsers(IPermissionManager mgr, int workspaceId, int artifactId, int groupId)
{
List<Relativity.Services.User.UserRef> users =
await mgr.GetItemGroupUsersAsync(workspaceId, artifactId, new GroupRef(groupId));
Console.WriteLine($"Users in group {groupId} with access to artifact {artifactId}:");
users.ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine($"{x.ArtifactID} - {x.Name}"));
}